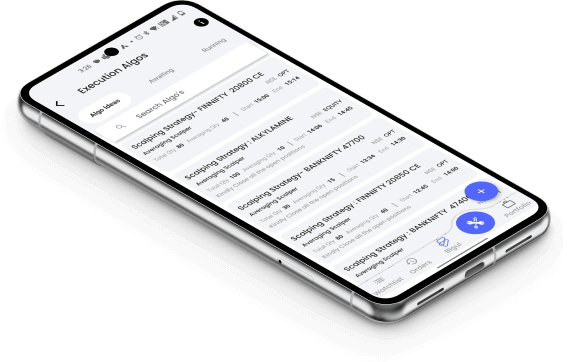
In India, there are several types of bonds available for investors. Some of the common types include:
1. Government Bonds
Government bonds in India are issued by the Government to raise funds for various needs like infrastructure development or managing fiscal deficits. Examples include:
- Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs)
- Government Securities (G-Secs)
- State Development Loans (SDLs).
They are considered relatively safe investments as they are backed by the government's creditworthiness and offer a rate of interest around 7–10%.
2. Corporate Bonds
Corporate Bonds are loans issued by companies to raise funds for their operations or expansion. Investors who purchase these bonds essentially lend money to the company and receive periodic interest payments in return.
Unlike government bonds, corporate bonds carry higher risk because they depend on the company's financial health. However, they often offer higher returns to compensate for the increased risk.
3. Municipal Bonds
Municipal bonds in India are issued by local governments to fund projects like building roads or schools. Investors buy these bonds to support their communities and earn interest on their investment.
Municipal bonds are considered safer than corporate bonds and may offer tax benefits to investors.
They are a way for individuals to contribute to local development while earning a return on their investment.
4. Callable Bonds
Callable bonds are like regular bonds, but with a twist: the issuer has the option to pay off the bond before its maturity date. This means they can repay the bond early if interest rates drop, saving them money.
However, for investors, this introduces the risk of having to reinvest the proceeds at potentially lower rates, affecting their overall returns.
5. Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) Bonds
PSU Bonds are issued by government-owned companies in India to raise funds. These bonds help PSUs finance their operations or expansion projects.
Investors buy these bonds, providing capital to the PSU, and in return, receive periodic interest payments along with the repayment of the principal amount at maturity.
These bonds are considered relatively safe investments due to the backing of the government.
6. Tax-Free Bonds
Tax-Free Bonds are special bonds issued by government entities or infrastructure companies. They offer interest income that is not subject to income tax, making them attractive to investors seeking tax-free returns.
These bonds are designed to encourage investment in specific sectors and provide a way for investors to earn income without worrying about taxes on their returns.
7. Zero-Coupon Bonds
Zero-coupon bonds are sold at a discounted price, meaning you pay less than the face value upfront.
They don't pay interest periodically. Instead, investors receive the full face value when the bond matures.
For instance, if you buy a ₹1,000 zero-coupon bond for ₹800, you get ₹1,000 when it matures, earning ₹200.
8. Convertible Bonds
Convertible Bonds are a type of bond that gives investors the option to convert their bond holdings into a specified number of equity shares of the issuing company. This conversion typically occurs after a predetermined period.
Investors can benefit from potential capital appreciation if the company's stock price rises, while still receiving fixed interest payments until conversion.
9. Floating-Rate Bonds
Floating-rate bonds in India have interest rates that vary based on a benchmark like the RBI repo rate. As this rate changes, so does the bond's interest payments.
For investors, this means potential fluctuations in income, offering some protection against interest rate changes compared to fixed-rate bonds.
It's a dynamic option that reflects current market conditions, providing flexibility in uncertain economic climates.
10. High-yield Bonds (Junk Bonds)
High-yield bonds are also known as junk bonds. They are issued by companies with lower credit ratings. They offer higher interest rates compared to investment-grade bonds to attract investors.
However, they come with higher risk of default, as the issuing companies may have financial instability.
Investors should be cautious as higher returns are balanced by increased risk of losing their investment if the issuing company fails to meet its obligations.