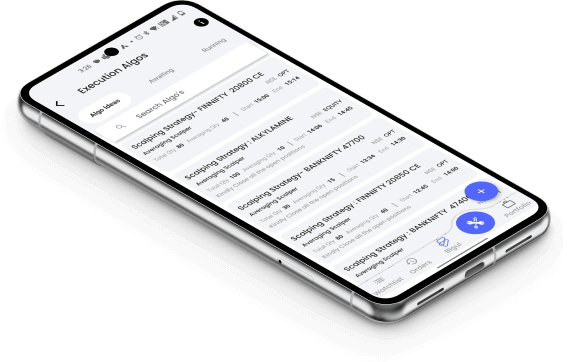
1. Trend-Following Pullback Strategy
In a trend-following pullback strategy, you identify a strong market trend and wait for temporary price reversals, known as pullbacks.
When the pullback shows signs of losing momentum, such as a decrease in selling pressure or a bounce off a key support level, you enter a trade in the direction of the overall trend.
This strategy aims to capitalize on the resumption of the trend after a temporary retracement, using technical indicators like SMA to confirm trend strength.
2. Support and Resistance Levels
Look for key price levels where the market has previously stalled or reversed. When the price retraces back to these levels, it can present a potential trading opportunity.
Confirm the significance of these levels with technical indicators or candlestick patterns. If the price holds at these levels, it could indicate a continuation of the trend or a reversal.
This strategy relies on identifying areas where buyers or sellers are likely to step in, providing a basis for entering or exiting trades.
3. Fibonacci Retracement Levels
In the Fibonacci retracement strategy, traders use key levels derived from Fibonacci ratios to anticipate price pullbacks. These levels, typically at 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8% retracements, indicate potential support or resistance zones.
When price retraces to these levels, traders look for confirmation signals such as candlestick patterns or other technical indicators to enter trades in the direction of the trend.
Combining Fibonacci retracement levels with other analysis tools enhances the probability of successful trades.
4. Volume Analysis
Watch the trading volume during a pullback. It should drop as prices retrace and increase when the trend resumes.
Low volume during a pullback suggests weakening momentum, while higher volume during the trend continuation confirms its strength. Monitoring volume helps you confirm the validity of the pullback and the likelihood of the trend persisting.
This confirmation improves your decision-making process, increasing the probability of successful trades.
5. Moving Averages
Use moving averages to spot trends and find entry points during pullbacks. Moving averages smooth out price data over a specified period, revealing the overall direction of the market.
For instance, during an uptrend, you'd wait for prices to dip toward the moving average before considering a buying opportunity. Common choices include the 20-period or 50-period moving averages.
This strategy helps you align with the trend while minimizing the risk of entering trades at unfavourable moments.
6. Candlestick Patterns
Look for specific candlestick patterns during pullbacks. For instance, a bullish engulfing or hammer candlestick in a downtrend can signal a potential upward reversal.
These patterns indicate a shift in sentiment among traders and can provide entry points for trades. By identifying these patterns, traders can capitalize on potential reversals or continuations of the trend.
However, it's important to confirm these signals with other technical indicators and exercise proper risk management to make informed trading decisions.
7. Horizontal Steps
The horizontal steps strategy involves observing the natural price movements that reflect the market's rhythm. These movements, resembling steps, occur during trending phases.
This approach pairs well with breakout strategies. If you miss the initial entry opportunity during a breakout pullback, horizontal steps offer alternative entry points as the trade unfolds.
Additionally, this strategy allows for safer stop-loss placement by waiting for the price to complete a step before adjusting the stop-loss behind the previous pullback area.