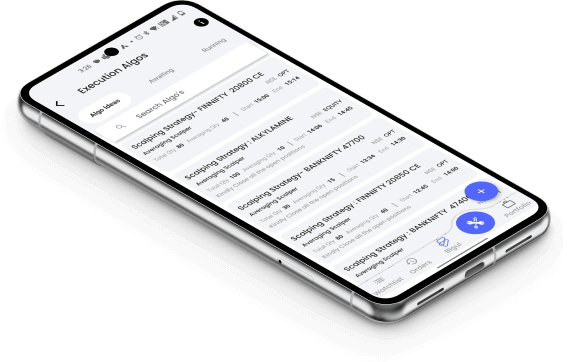
Forex trading means trading currencies, like swapping Indian Rupees for US Dollars. It happens worldwide 24/5, so you can trade anytime.
Stock trading, on the other hand, deals with buying and selling shares of companies, such as purchasing stocks of Indian companies like Infosys or Reliance. Stocks are traded on exchanges like the NSE and BSE in India, during specific hours on weekdays.
So, Forex focuses on currencies traded worldwide continuously, while stocks involve buying ownership in specific companies during market hours.
2. Market Hours
Forex markets are open for 24 hours 5 days a week, allowing trading throughout the day from Monday to Friday, providing flexibility for traders to engage at any time.
On the other hand, Indian stock markets, like the NSE and BSE, operate during specific hours on weekdays, generally from 9:15 AM to 3:30 PM IST.
This means that stock trading in India is confined to these set hours, unlike Forex trading, which offers continuous opportunities for trading due to its round-the-clock nature.
3. Liquidity
Forex markets trade currencies globally, offering high liquidity due to continuous trading. This means traders can easily buy or sell currencies without significant price changes.
Conversely, stock markets in India operate within specific hours and may vary in liquidity. While major stocks usually have good liquidity, smaller ones might not. Liquidity affects how quickly assets can be bought or sold without causing substantial price changes.
In Forex, high liquidity ensures efficient trading, while stock traders need to consider liquidity levels to execute trades smoothly, especially with less-traded stocks.
4. Asset Variety
In Forex trading, you trade currency pairs like EUR/USD or USD/INR. It's all about exchanging one currency for another, aiming to profit from fluctuations in their exchange rates.
On the other hand, equity trading involves buying and selling shares of individual companies listed on stock exchanges like the BSE or NSE in India.
So, while Forex focuses solely on currency pairs, stock trading offers a wider variety of assets, including shares of companies across different sectors and industries, providing traders with more options for investment.
5. Regulation
In India, both Forex and stock trading are regulated activities overseen by government bodies like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). These regulations aim to ensure fair trading practices, investor protection, and market integrity.
For Forex trading, there are limits on the amount of currency you can trade and restrictions on leverage usage.
Similarly, stock trading is subject to rules set by SEBI, including guidelines on trading practices, disclosures, and investor education.
Understanding and sticking to these regulations is essential to participate safely and legally in both markets.
6. Volatility
In stock trading, the prices of individual company shares can swing up and down, but the overall market tends to be steadier compared to Forex trading.
Forex, on the other hand, involves trading currency pairs, and their values can change rapidly, especially during important economic events. This means Forex trading often sees bigger price swings or fluctuations.
So, while both markets have their share of ups and downs, Forex tends to have more pronounced price movements, making it potentially riskier. However, it also offers higher profit opportunities if you're prepared to handle the volatility.
7. Trading Costs
In stock trading, you'll likely encounter more fees compared to Forex. Brokers often charge commissions, taxes, and other costs for buying and selling stocks. These fees can plie up and extract a great sum out of your overall profits profits.
Conversely, Forex trading typically involves lower transaction costs since brokers commonly don't charge commissions. Instead, you may encounter spreads, which are the differences between buying and selling prices for currency pairs.
Understanding these cost differences is important as it helps you manage expenses and make more informed decisions about which market suits your trading style and budget.
8. Market Influences
Stock trading is affected by various factors like company news, industry trends, and global market conditions. For example, if a company announces strong earnings, its stock price may increase.
On the flip side, negative news or economic downturns can lead to declines. Industry trends, such as technological advancements, also impact stock prices. Additionally, global events like geopolitical tensions or natural disasters can influence market sentiment and stock prices.
Being aware of these influences helps you make informed decisions when buying or selling stocks, ensuring you consider both internal and external factors affecting the market.