Comparative Report on NPA Improvement and Its Impact on Interest Rate-Sensitive Sectors
Introduction
Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) have historically been a significant concern for the Indian banking sector, impacting asset quality, liquidity, and profitability. However, recent trends indicate a marked improvement in NPAs across several key Indian banks, suggesting better asset quality management, economic recovery, and effective regulatory measures. This report provides a detailed analysis of NPA improvements in major Indian banks, the drivers behind these improvements, and the positive impact on interest rate-sensitive sectors such as automobiles, housing, and consumer durables. Additionally, it includes a comparative study of banks with improved metrics and those with declining earnings and increasing NPAs.
Overview of NPA Improvement in Key Indian Banks
Recent quarterly earnings from major Indian banks reveal a notable reduction in NPAs, reflecting an improved financial position. The reduction enhances the stability of the banking system, increases liquidity, and provides favorable financing conditions for interest rate-sensitive sectors.
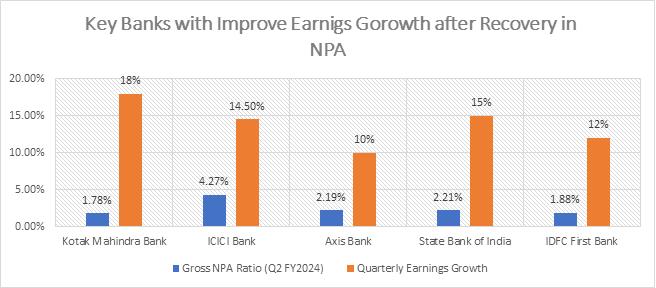
| Bank | Gross NPA Ratio (Q2 FY2024) | Quarterly Earnings Growth | Reasons for Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kotak Mahindra Bank | 1.78% | +18% | Strong risk management, diversified loan portfolio, effective recovery mechanisms. |
| ICICI Bank | 4.27% | +14.5% | Focus on high-quality corporate and retail portfolios, increased net profit. |
| Axis Bank | 2.19% | +10% | Enhanced monitoring of large corporate accounts, strong asset quality management. |
| State Bank of India | 2.21% | +15% | Improved recovery through restructuring and IBC resolutions, lower provisioning. |
| IDFC First Bank | 1.88% | +12% | Strong asset quality due to cautious expansion in retail and SME segments, aggressive loan recovery. |
Comparative Study: Improved vs. Declining Banks
A comparative analysis highlights key differentiators between banks improving their earnings and NPA metrics and those facing challenges.
| Category | Banks with Improved Metrics | Banks with Declining Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Earnings Growth | Positive growth (10% or more). | Negative or marginal growth in earnings. |
| NPA Trend | Declining NPAs consistently. | Rising or stagnant NPA levels. |
| Asset Quality Management | Strong recovery mechanisms, diversified portfolios. | Limited recovery efficiency, higher exposure to stressed sectors. |
| Liquidity Position | Improved liquidity due to better NPA management. | Constrained liquidity due to higher provisioning requirements. |
| Examples | Kotak Mahindra Bank, ICICI Bank, SBI | Punjab National Bank (PNB), Central Bank of India, Union Bank of India. |
Banks with Declining Earnings and Increasing NPAs (Examples)
Punjab National Bank (PNB)
Gross NPA Ratio:
~6.5% (Q2 FY2024)Earnings Growth:
Decline of ~8% YoYKey Factors:
Higher exposure to stressed sectors, limited efficiency in recovery frameworks, and rising provisioning.
Central Bank of India
Gross NPA Ratio:
~8.2% (Q2 FY2024)Earnings Growth:
Marginal or negative growthKey Factors:
Legacy NPAs from infrastructure and construction sectors, weak retail loan growth.
Union Bank of India
Gross NPA Ratio:
~6.85% (Q2 FY2024)Earnings Growth:
Slight decline or stagnation.Key Factors:
High exposure to corporate loans in stressed industries and delays in recovery mechanisms.
UCO Bank
Gross NPA Ratio:
~6.7% (Q2 FY2024)Earnings Growth:
Marginal growth (~2-3% YoY).Key Factors:
Limited retail and SME diversification, slower resolution of NPAs.
Key Drivers Behind NPA Improvement
1. Economic Recovery
- Improved repayment capacity due to economic rebound, especially in manufacturing, services, and agriculture.
- Source: Indian Economic Recovery - Business Standard
2. Regulatory Support
- RBI initiatives, including liquidity support and rate cuts (e.g., 50 bps CRR cut in December 2024).
- Source: RBI Monetary Policy - Reuters
3. Enhanced Recovery Frameworks
- Use of mechanisms like the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) and One-Time Restructuring (OTR).
- Source: IBC Recovery Insights - Economic Times
4. Improved Lending Practices
- Focus on retail and SME loans while reducing exposure to high-risk sectors like construction and infrastructure.
- Source: Banking Sector Trends - Mint
Banks with Declining Earnings and Increasing NPAs
| Bank Name | Gross NPA Ratio (Q2 FY2024) | Earnings Growth | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Punjab National Bank | ~6.5% | Decline of ~8% YoY | Higher exposure to stressed sectors, limited efficiency in recovery frameworks, and rising provisioning. |
| Central Bank of India | ~8.2% | Marginal or negative | Legacy NPAs from infrastructure and construction sectors, weak retail loan growth. |
| Union Bank of India | ~6.85% | Slight decline | High exposure to corporate loans in stressed industries and delays in recovery mechanisms. |
| UCO Bank | ~6.7% | Marginal (~2-3%) | Limited retail and SME diversification, slower resolution of NPAs. |
Impact on Interest Rate-Sensitive Sectors
The reduction in NPAs has positively impacted liquidity, credit availability, and borrowing costs, driving growth in key sectors:
1. Automobile Sector
- Improved financing options and lower loan interest rates have driven recovery in passenger and commercial vehicle sales.
Examples:
Maruti Suzuki (growth in car sales), Tata Motors (global expansion).Source:
Automobile Sector Report - Moneycontrol
2. Housing and Real Estate
- Increased access to home loans has fueled demand, especially in mid and premium segments.
Examples:
DLF Limited (residential sales growth), Godrej Properties (expansion in premium housing).Source:
Housing Market Insights - Knight Frank
3. Consumer Durables
- Easier financing options have boosted sales in home appliances and electronics.
Examples:
Voltas (AC demand), Havells India (electrical appliances growth).Source:
Consumer Durables Market Report - CRISIL
Economic and Market Outlook
1. Improved Banking Metrics
Better asset quality positions banks for increased lending, driving liquidity into the economy.2. Interest Rate Trends
RBI’s rate cuts improve credit availability and lower borrowing costs, benefiting sectors reliant on loans.3. Investor Confidence
Stability in banking and growth in key sectors are fostering optimism among investors.
Conclusion
The improvement in NPAs across Indian banks underscores a shift towards better asset quality management and financial discipline. This has enhanced liquidity, reduced interest rates, and positively impacted borrowing-sensitive sectors such as automobiles, housing, and consumer durables.
Recommendations
Banking Sector:
Monitor NPA trends and loan disbursement metrics for investment opportunities.Interest Rate-Sensitive Sectors:
Focus on companies benefiting from improved credit conditions and consumer confidence.
